Shifting Letters II
Problem Description
You are given a string s of lowercase English letters and a 2D integer array shifts where shifts[i] = [start i, end i, direction i]. For every i, shift the characters in s from the index start i to the index end i (inclusive) forward if direction i = 1, or shift the characters backward if direction i = 0.
Shifting a character forward means replacing it with the next letter in the alphabet (wrapping around so that 'z' becomes 'a'). Similarly, shifting a character backward means replacing it with the previous letter in the alphabet (wrapping around so that 'a' becomes 'z').
Return the final string after all such shifts to s are applied.
Explanation
We are given a string s and an array shifts that contains multiple shift instructions. Each instruction tells us to shift certain parts of the string either forward (to the next letter) or backward (to the previous letter).
Our goal is to apply all these shifts to the string and return the final result.
Examples
Input: s = "abc", shifts = [[0,1,0],[1,2,1],[0,2,1]]
Output: "ace"
Explanation: Firstly, shift the characters from index 0 to index 1 backward. Now s = "zac".
Secondly, shift the characters from index 1 to index 2 forward. Now s = "zbd".
Finally, shift the characters from index 0 to index 2 forward. Now s = "ace".
Input: s = "dztz", shifts = [[0,0,0],[1,1,1]]
Output: "catz"
Explanation: Firstly, shift the characters from index 0 to index 0 backward. Now s = "cztz".
Finally, shift the characters from index 1 to index 1 forward. Now s = "catz".
Constraints
- 1 <= s.length, shifts.length <= 5 * 10^4
- shifts[i].length == 3
- 0 <= start i <= end i < s.length
- 0 <= direction i <= 1
- s consists of lowercase English letters.
This problem description is a simulation-based question where we are given few queries with each query having the start , end and direction information using which we have to alter the string and return the final string!! Let's implement the first intuitive approach !!
Brute Force Approach
Intuition
The brute force approach is, we will iterate the shifts[][] query and extract the required information i.e. the start, end and direction.
Next, we pick up the first character of string s and iterate from start to end
For each shift, we iterate over the part of the string from index start to end. If the direction is 1 (forward), we replace each character with the next letter in the alphabet. If we reach 'z', we wrap around to 'a'.
If the direction is 0 (backward), we move each character to the previous letter. If the character is 'a', it wraps around to 'z'. This process is repeated for every shift instruction in the array.
Once, we are done iterating the whole shifts[][] , we return the final altered string.
Approach
Step 1: Convert string s to a character array result.
Step 2: Iterating the Shifts [][] : Extract start, end, and direction from the current shift.
Loop from index start to end (inclusive):
- If direction is 1 (forward shift):
1. Replace the character at index i with the next letter in the alphabet.
2. If the character is 'z', wrap around to 'a'. - If direction is 0 (backward shift):
1. Replace the character at index i with the previous letter in the alphabet.
2. If the character is 'a', wrap around to 'z'.
Step 3: Convert the modified character array back to a string and return the final string.
Dry-Run
s = "abcdef"
shifts = [
[0, 3, 1], // Increment indices 0 to 3
[1, 4, 0], // Decrement indices 1 to 4
[2, 5, 1] // Increment indices 2 to 5
]
Initial state:
s = "abcdef"
result = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f']
Step 1: Process shift [0, 3, 1] (increment indices 0 to 3)
- Increment result[0] ('a'): 'a' → 'b'
- Increment result[1] ('b'): 'b' → 'c'
- Increment result[2] ('c'): 'c' → 'd'
- Increment result[3] ('d'): 'd' → 'e'
Updated result: ['b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'e', 'f']
Step 2: Process shift [1, 4, 0] (decrement indices 1 to 4)
- Decrement result[1] ('c'): 'c' → 'b'
- Decrement result[2] ('d'): 'd' → 'c'
- Decrement result[3] ('e'): 'e' → 'd'
- Decrement result[4] ('e'): 'e' → 'd'
Updated result: ['b', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'd', 'f']
Step 3: Process shift [2, 5, 1] (increment indices 2 to 5)
- Increment result[2] ('c'): 'c' → 'd'
- Increment result[3] ('d'): 'd' → 'e'
- Increment result[4] ('d'): 'd' → 'e'
- Increment result[5] ('f'): 'f' → 'g'
Updated result: ['b', 'b', 'd', 'e', 'e', 'g']
Final Result:
Join the result array to get the final string:
"bbdeeg"
Output: "bbdeeg"
Brute Force in all Languages
1. C++ Try on Compiler
class Solution {
public:
string shiftingLetters(string s, vector<vector<int>>& shifts) {
// Convert the string to a character array
vector<char> result(s.begin(), s.end());
// Loop through each shift instruction
for (auto shift : shifts) {
// Extract the start, end, and direction values
int start = shift[0];
int end = shift[1];
int direction = shift[2];
// Apply the shift to the characters in the specified range
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
// Shift forward if direction == 1
if (direction == 1) {
result[i] = (result[i] - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a';
// Shift backward if direction == 0
} else {
result[i] = (result[i] - 'a' - 1 + 26) % 26 + 'a';
}
}
}
// Return the final modified string
return string(result.begin(), result.end());
}
};2. Java Try on Compiler
public class Solution {
public String shiftingLetters(String s, int[][] shifts) {
// Convert the string to a character array
char[] result = s.toCharArray();
// Loop through each shift instruction
for (int[] shift : shifts) {
// Extract the start, end, and direction values
int start = shift[0];
int end = shift[1];
int direction = shift[2];
// Apply the shift to the characters in the specified range
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
// Shift forward if direction == 1
if (direction == 1) {
result[i] = (char) ((result[i] - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a');
// Shift backward if direction == 0
} else {
result[i] = (char) ((result[i] - 'a' - 1 + 26) % 26 + 'a');
}
}
}
// Return the final modified string
return new String(result);
}
}
3. Python Try on Compiler
class Solution:
def shiftingLetters(self, s: str, shifts: list[list[int]]) -> str:
# Convert the string to a list of characters
result = list(s)
# Loop through each shift instruction
for shift in shifts:
# Extract the start, end, and direction values
start, end, direction = shift
# Apply the shift to the characters in the specified range
for i in range(start, end + 1):
# Shift forward if direction == 1
if direction == 1:
result[i] = chr((ord(result[i]) - ord('a') + 1) % 26 + ord('a'))
# Shift backward if direction == 0
else:
result[i] = chr((ord(result[i]) - ord('a') - 1 + 26) % 26 + ord('a'))
# Return the final modified string
return ''.join(result)
4. JavaScript Try on Compiler
var shiftingLetters = function(s, shifts) {
// Convert the string to a character array
let result = s.split('');
// Loop through each shift instruction
for (let shift of shifts) {
// Extract the start, end, and direction values
let start = shift[0];
let end = shift[1];
let direction = shift[2];
// Apply the shift to the characters in the specified range
for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) {
// Shift forward if direction == 1
if (direction == 1) {
result[i] = String.fromCharCode((result[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'a'.charCodeAt(0) + 1) % 26 + 'a'.charCodeAt(0));
// Shift backward if direction == 0
} else {
result[i] = String.fromCharCode((result[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'a'.charCodeAt(0) - 1 + 26) % 26 + 'a'.charCodeAt(0));
}
}
}
// Return the final modified string
return result.join('');
};Time Complexity: O(n*m)
Outer Loop: The outer loop iterates over the shifts array. If there are m shift operations, the loop will run m times.
Inner Loop: For each shift operation, the inner loop iterates from start to end (inclusive). In the worst case, this loop will iterate over the entire string s (length n).
Hence, the overall time complexity is: O(m×n)
where m = Number of shift operations , n = Length of the string.
Space Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space Complexity refers to the extra space required in the algorithm other than the input space
Character Array: We use a character array result to store the modified version of the string. This array requires space proportional to the length of the string which takes O(n) space.
Shift Array (Input): The shifts array is provided as input and doesn't count toward auxiliary space.
Other Variables: A few variables (start, end, direction, i) are used. This is constant space which is O(1).
The overall Auxiliary space complexity is: O(n)
Total Space Complexity: The total space complexity is a combination of the auxiliary space and input space.
Input space: The shifts array takes O(m) space.
Auxiliary space: The result array takes O(n) space.
Hence, the total space complexity is: O(n+m) + O(n) = O(n+m)
If we analyse the brute force code with few other test-cases. We will get the test-cases where the same range of letters will be altered which will result in time limit exceeded due to the constraints size. We need to figure out a optimal approach !!
Optimal Approach
Intuition
Before we move to the optimal approach, let's analyze what parts of the brute-force method need optimization. In the brute-force approach, we notice that each letter of the string s can be affected multiple times by different queries. For example, if we have s = "abcd" and queries like [0,1,0], [0,2,1], [0,3,1], we see that the character 'a' is modified three times. This repetition happens for other characters too, leading to a time complexity of O(n²) due to nested loops processing each query individually.
Now, let’s think about how to handle this more efficiently. For a moment lets just assume we can only increment characters e.g., s = "abcdefgh" and query [0,3,1]. This query asks us to increment each character by 1 from index 0 to 3.
So, instead of manually incrementing each character in the range, we have to apply a smart trick.
Can we use flags to mark the start and stop points of the changes?
For the query [0,3,1], we can place a green flag at index 0, indicating that increments should start here and can place a red flag at index 4 (end index + 1), indicating that increments should stop before this index.
If we visualize this process, the green flag means "start adding 1," and the red flag means "stop adding 1."
For multiple such queries, we add +1 for green flags and -1 for red flags at the respective indices. For instance, for queries [0,3,1], [0,2,1], [1,2,1], the resulting flags on a number line look like this.
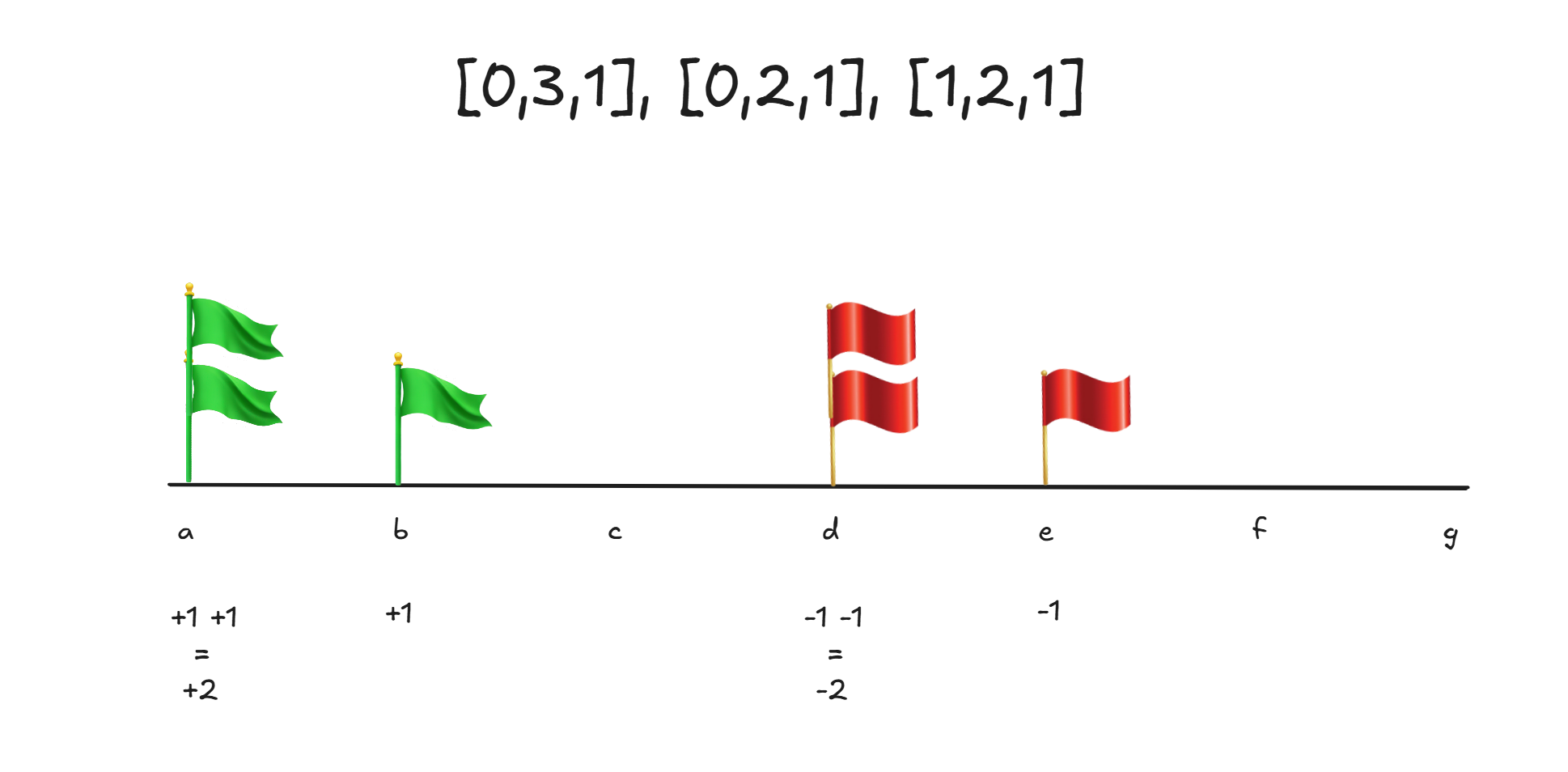
Now, the logic begins on how to make use of it?
Let's do one thing, let's maintain a runningSum initialized with 0. Whenever we encounter a green flag we will add +1 to the runningSum.
Why are we maintaining a runningSum?
The running sum tells us the cumulative effect of all active queries at each index
- At index 0, a becomes a + 2 = c.
- At index 1, b becomes b + 3 = e.
- At index 2, c becomes c + 3 = f.
- At index 3, d becomes d + 1 = e.
This process avoids repeatedly looping over the same range for every query. Instead, we place flags and calculate the cumulative effect in O(n) time using a prefix sum approach and since we sweep down the effects from start to end we call this as the line sweep algorithm.
So, what we will be doing is
We start by creating a difference array update[] of size n + 1, where n is the length of the string s. This array will be used to mark where to start and stop increments based on the queries.For a query [start, end, direction]: If direction == 1 (increment), we add +1 at update[start] and subtract 1 at update[end + 1]. If direction == 0 (decrement), we subtract 1 at update[start] and add 1 at update[end + 1].
Once all queries are processed, we compute the prefix sum of the diff array. The prefix sum at index i gives the net effect (increment or decrement) for the character at index i in the string. This step ensures that all overlapping queries are accounted for.ApproachStep 1: We will convert the string s into a character array result.Step 2: For each query in shifts: Extract start, end, and direction: For each index from start to end:If direction is 1, increment the character at that index by 1 in a cyclic manner within 'a' to 'z'.If direction is 0, decrement the character at that index by 1 in a cyclic manner within 'a' to 'z'.Step 3: Convert the modified character array result back to a string. Print the resulting string.
Dry-Run
s = "abcdef"
shifts = [
[0, 3, 1], // Increment indices 0 to 3
[1, 4, 0], // Decrement indices 1 to 4
[2, 5, 1] // Increment indices 2 to 5
]
Step 1: Initialize Variables
- n = 6 (length of s)
- update = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] (size n + 1, initially all zeros)
Step 2: Process Each Query
Query [0, 3, 1] (Increment from index 0 to 3):
- update[0] += 1 → update[0] = 1
- update[4] -= 1 → update[4] = -1
- update = [1, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0, 0]
Query [1, 4, 0] (Decrement from index 1 to 4):
- update[1] -= 1 → update[1] = -1
- update[5] += 1 → update[5] = 1
- update = [1, -1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0]
Query [2, 5, 1] (Increment from index 2 to 5):
- update[2] += 1 → update[2] = 1
- update[6] -= 1 → update[6] = -1
- update = [1, -1, 1, 0, -1, 1, -1]
Step 3: Calculate Prefix Sum and Modify String
- Initialize change = 0 and ans = "".
- Iterate through the string s:
Index 0 (Character: 'a'):
- change += update[0] → change = 1
- newChar = ('a' - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a' = 'b'
- ans = "b"
Index 1 (Character: 'b'):
- change += update[1] → change = 0
- newChar = ('b' - 'a' + 0) % 26 + 'a' = 'b'
- ans = "bb"
Index 2 (Character: 'c'):
- change += update[2] → change = 1
- newChar = ('c' - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a' = 'd'
- ans = "bbd"
Index 3 (Character: 'd'):
- change += update[3] → change = 1
- newChar = ('d' - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a' = 'e'
- ans = "bbde"
Index 4 (Character: 'e'):
- change += update[4] → change = 0
- newChar = ('e' - 'a' + 0) % 26 + 'a' = 'e'
- ans = "bbdee"
Index 5 (Character: 'f'):
- change += update[5] → change = 1
- newChar = ('f' - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a' = 'g'
- ans = "bbdeeg"
Output: "bbdeeg"
Optimal Code in all Languages
1. C++ Try on Compiler
class Solution {
public:
string shiftingLetters(string s, vector<vector<int>>& shifts) {
// Get the length of the string
int n = s.length();
// Create an array to track the cumulative shifts
vector<int> update(n + 1, 0);
// Process each shift operation
for (auto& shift : shifts) {
// Extract start, end, and direction of the shift
int start = shift[0];
int end = shift[1];
int dir = shift[2];
// Update the `update` array based on direction
if (dir == 0) {
update[start] -= 1;
update[end + 1] += 1;
} else {
update[start] += 1;
update[end + 1] -= 1;
}
}
// Variable to keep track of accumulated shifts
int change = 0;
// String to construct the result
string ans = "";
// Apply the cumulative shifts to each character
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Update the cumulative shift
change += update[i];
// Calculate the new character after applying the shift
char newChar = (s[i] - 'a' + change % 26 + 26) % 26 + 'a';
// Append the shifted character to the result
ans += newChar;
}
// Return the final shifted string
return ans;
}
};2. Java Try on Compiler
class Solution {
public String shiftingLetters(String s, int[][] shifts) {
// Get the length of the string
int n = s.length();
// Create an array to track the cumulative shifts
int[] update = new int[n + 1];
// Process each shift operation
for (int[] shift : shifts) {
// Extract start, end, and direction of the shift
int start = shift[0];
int end = shift[1];
int dir = shift[2];
// Update the `update` array based on direction
if (dir == 0) {
update[start] -= 1;
update[end + 1] += 1;
} else {
update[start] += 1;
update[end + 1] -= 1;
}
}
// Variable to keep track of accumulated shifts
int change = 0;
// StringBuilder to construct the result
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
// Apply the cumulative shifts to each character
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Update the cumulative shift
change += update[i];
// Calculate the new character after applying the shift
int newChar = (s.charAt(i) - 'a' + change % 26 + 26) % 26 + 'a';
// Append the shifted character to the result
ans.append((char) newChar);
}
// Return the final shifted string
return ans.toString();
}
}
3. Python Try on Compiler
class Solution:
def shiftingLetters(self, s: str, shifts: list[list[int]]) -> str:
# Get the length of the string
n = len(s)
# Create an array to track the cumulative shifts
update = [0] * (n + 1)
# Process each shift operation
for start, end, dir in shifts:
# Update the `update` array based on direction
if dir == 0:
update[start] -= 1
update[end + 1] += 1
else:
update[start] += 1
update[end + 1] -= 1
# Variable to keep track of accumulated shifts
change = 0
# Apply the cumulative shifts to each character
ans = []
for i in range(n):
# Update the cumulative shift
change += update[i]
# Calculate the new character after applying the shift
new_char = chr((ord(s[i]) - ord('a') + change % 26 + 26) % 26 + ord('a'))
# Append the shifted character to the result
ans.append(new_char)
# Return the final shifted string
return ''.join(ans)4. JavaScript Try on Compiler
var shiftingLetters = function(s, shifts) {
// Get the length of the string
const n = s.length;
// Create an array to track the cumulative shifts
const update = new Array(n + 1).fill(0);
// Process each shift operation
for (const [start, end, dir] of shifts) {
// Update the `update` array based on direction
if (dir === 0) {
update[start] -= 1;
update[end + 1] += 1;
} else {
update[start] += 1;
update[end + 1] -= 1;
}
}
// Variable to keep track of accumulated shifts
let change = 0;
// Array to construct the result
let ans = [];
// Apply the cumulative shifts to each character
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Update the cumulative shift
change += update[i];
// Calculate the new character after applying the shift
const newChar = String.fromCharCode((s.charCodeAt(i) - 'a'.charCodeAt(0) + change % 26 + 26) % 26 + 'a'.charCodeAt(0));
// Append the shifted character to the result
ans.push(newChar);
}
// Return the final shifted string
return ans.join('');
};Time Complexity: O(m + n)
Processing the shifts:
The for loop processes all shift operations. If there are m shift operations in the shifts array, the loop runs m times.
Time complexity for this step: O(m)
Updating the string:
The second loop iterates over each character of the string s (of length n) to compute the new characters based on the cumulative shifts.
Time complexity for this step: O(n)
Thus, the total time complexity is:
O(m + n)
Space Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space Complexity refers to the extra space required by an algorithm other than the input space.
- Shift update array:
An update array of size n + 1 is used to track the cumulative shifts. This array uses O(n) space. - Answer string:
The String is used to construct the result string. It uses O(n) space to store the final shifted string.
Thus, the auxiliary space complexity is: O(n)
Total Space Complexity:
Input storage:
The input includes the string s (size n) and the shifts array , both of which are provided externally but contribute to the total space which accumulates O(n) space
Auxiliary space: O(n)
Thus, the total space complexity is: O(n) + O(n) = O(2n) = O(n)