Print Each Element and its Index in an Array Solution in C++/Java/Python/JS
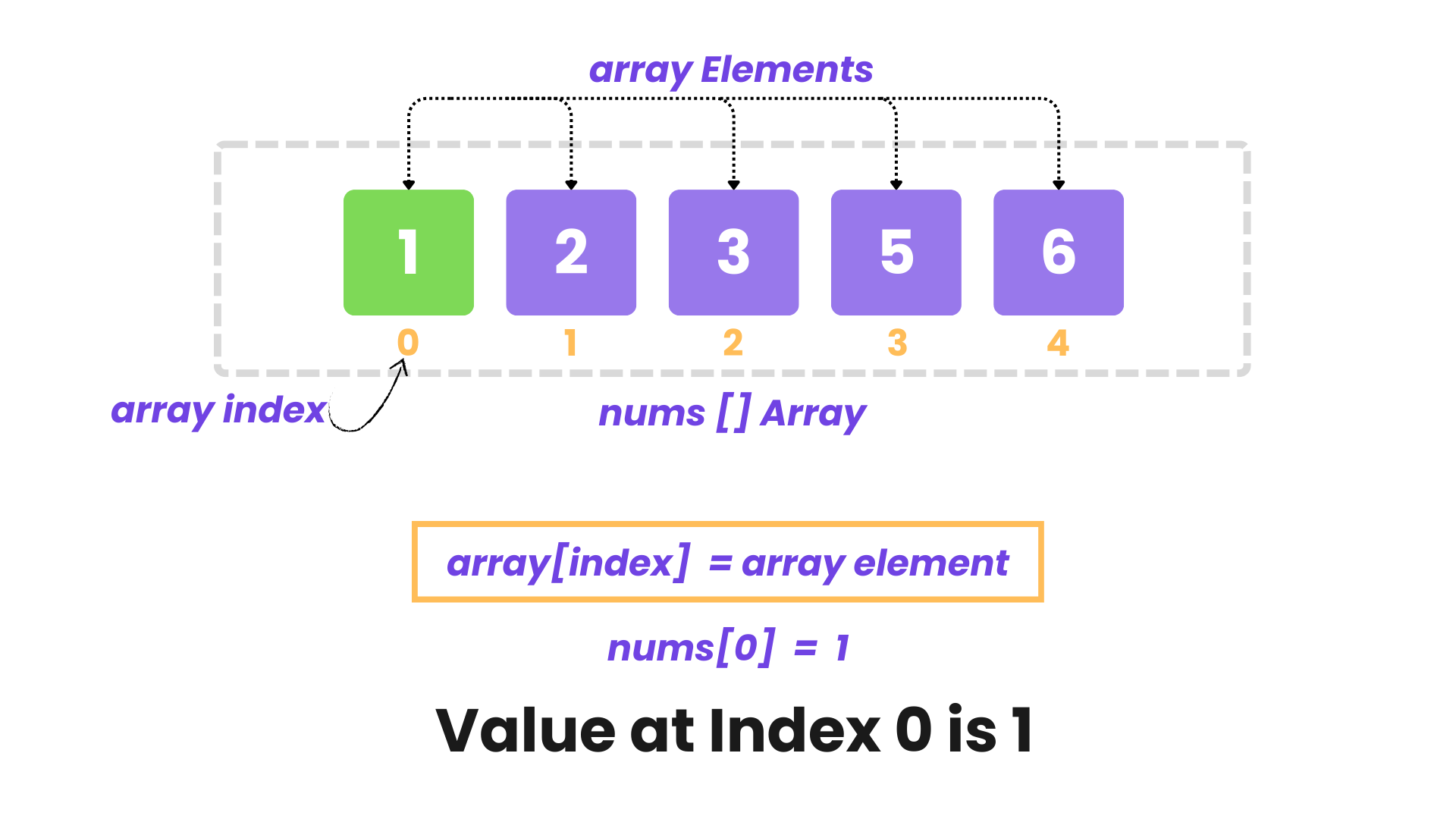
Write a program that takes an array as input and prints each element of the array along with its corresponding index.
Example:
Input: nums = [1, 2, 3, 5, 6]
Output:
Value at Index 0 is 1
Value at Index 1 is 2
Value at Index 2 is 3
Value at Index 3 is 5
Value at Index 4 is 6
Input: nums = [2, 1, 3, 3]
Output:
Value at Index 0 is 2
Value at Index 1 is 1
Value at Index 2 is 3
Value at Index 3 is 3
Approach
To solve this problem, we need to print both the index and the value of each element in the array. Since arrays use 0-based indexing, the indices go from 0, 1, 2, and so on up to n - 1, where n is the size of the array. If we know the index, we can get the corresponding value using nums[index]. So, all we need to do is go through every index from 0 to n - 1 using a loop, and for each index, print both the index and the value at that position.
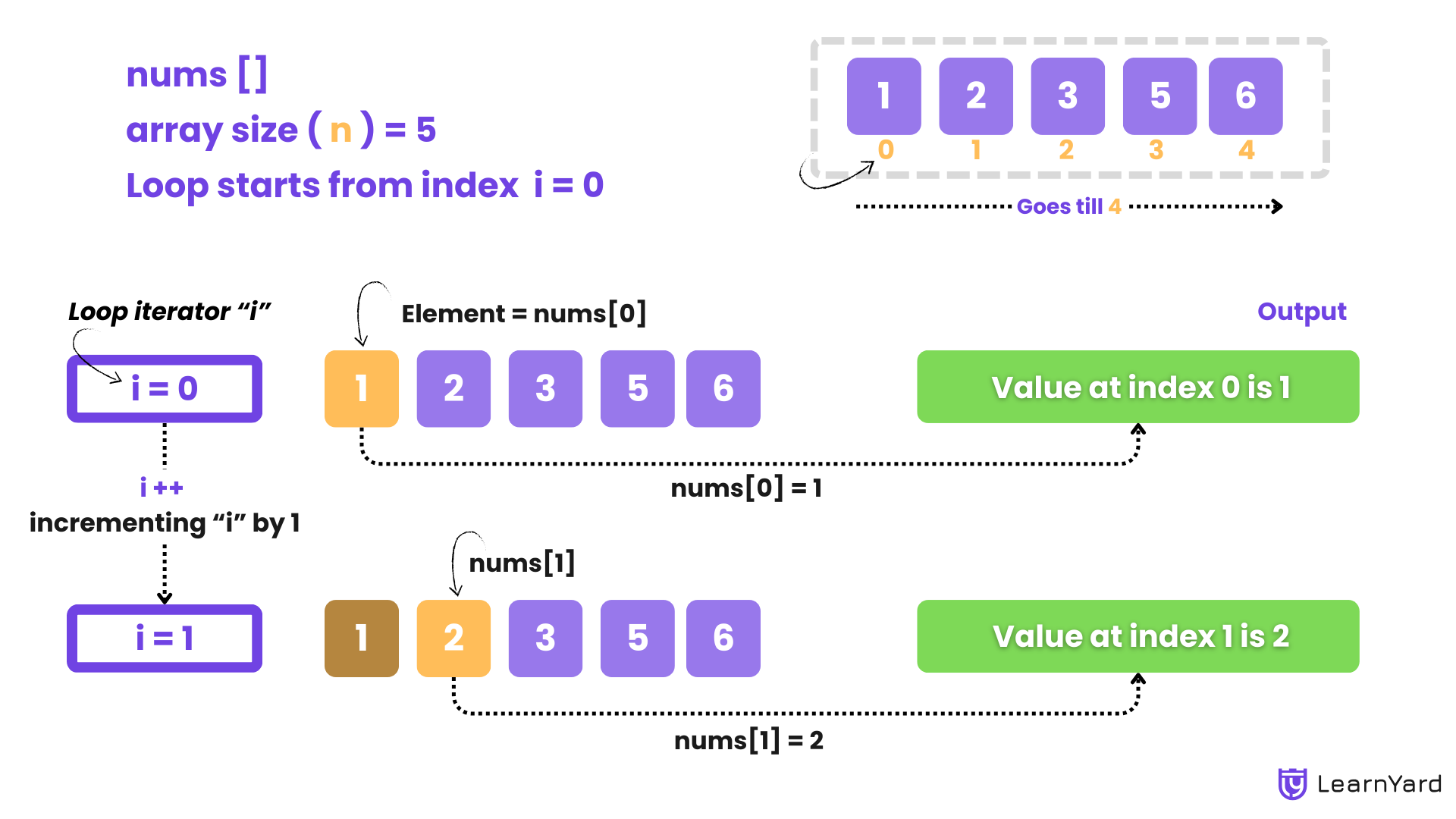
Dry Run
- Array nums contains [1, 2, 3, 5, 6].
- The size of the array is calculated as size = 5.
- The for loop starts with index = 0 and continues until index < size (i.e., index < 5).
Iterations of the Loop:
- First Iteration (index = 0):
The value at nums[0] is 1.
Output: Value at Index 0 is 1 - Second Iteration (index = 1):
The value at nums[1] is 2.
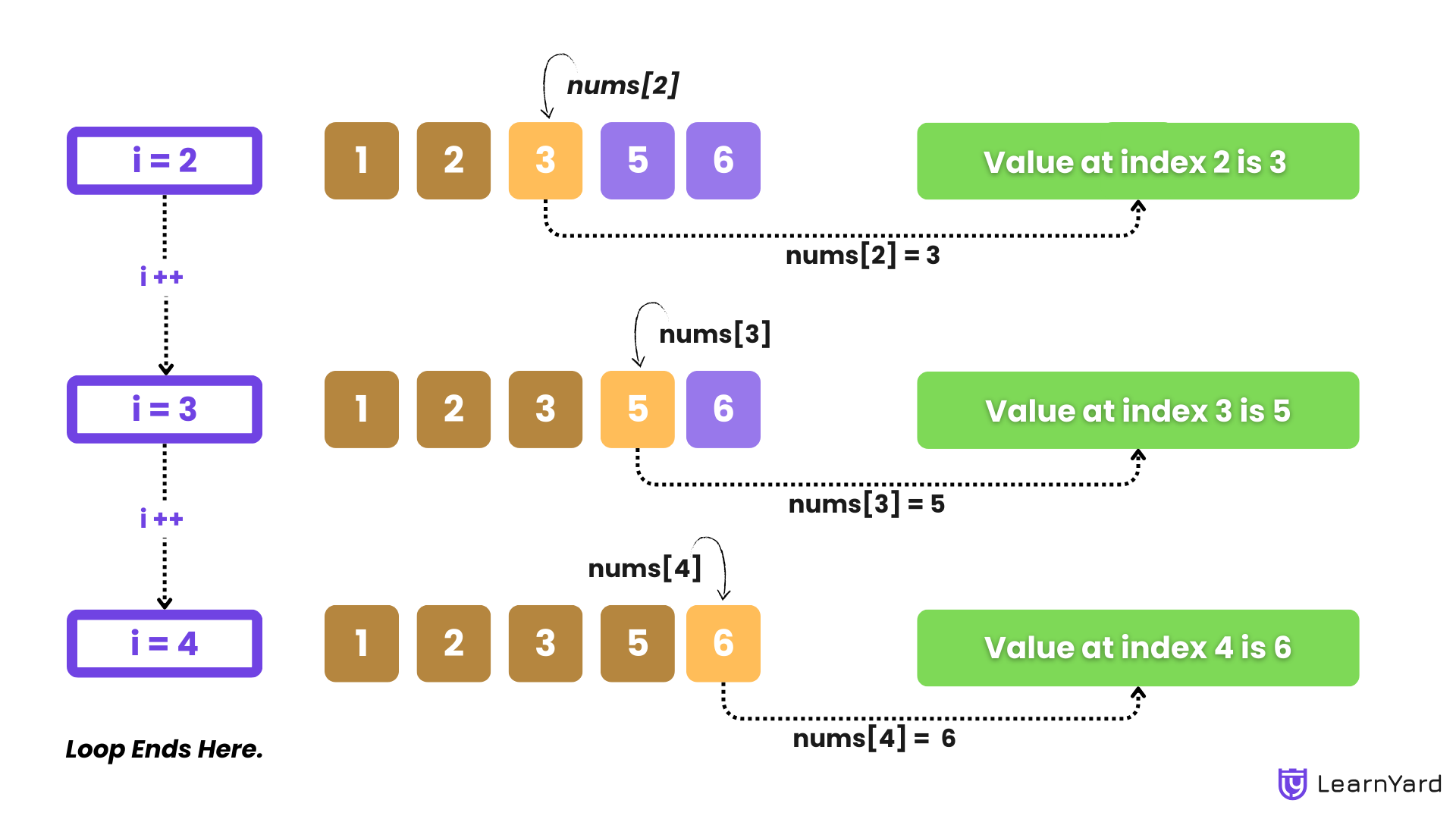
Output: Value at Index 1 is 2 - Third Iteration (index = 2):
The value at nums[2] is 3.
Output: Value at Index 2 is 3 - Fourth Iteration (index = 3):
The value at nums[3] is 5.
Output: Value at Index 3 is 5 - Fifth Iteration (index = 4):
The value at nums[4] is 6.
Output: Value at Index 4 is 6
End of Loop: The loop terminates when index becomes 5, which is not less than size (5).
Code for All Languages
C++
// Program to Print Each Element of an Array Along with Its Corresponding Index
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to print each element of the array along with its index
void printArrayWithIndices(int nums[], int size) {
// Loop through the array to print each element and its index
for (int index = 0; index < size; ++index) {
// Print the value at the current index
cout << "Value at Index " << index << " is " << nums[index] << endl;
}
}Java
// Program to Print Each Element of an Array Along with Its Corresponding In
import java.util.Scanner;
// Function to print each element of the array along with its index
public static void printArrayWithIndices(int[] nums) {
for (int index = 0; index < nums.length; ++index) {
System.out.println("Value at Index " + index + " is " + nums[index]);
}
Python
# Program to Print Each Element of an Array Along with Its Corresponding In
# Function to print each element of the array along with its index
def print_array_with_indices(nums):
for index, value in enumerate(nums):
print(f"Value at Index {index} is {value}")
Javascript
// Program to Print Each Element of an Array Along with Its Corresponding In
// Function to print each element of the array along with its index
function printArrayWithIndices(nums) {
for (let index = 0; index < nums.length; ++index) {
console.log(`Value at Index ${index} is ${nums[index]}`);
}
}Time Complexity : O(n)
The time complexity of this program is O(n), where n is the number of elements in the array. Since the program iterates through the entire array exactly once, performing a constant-time operation (printing) for each element. Since the loop runs n times, the overall time complexity is linear with respect to the size of the array.
Space Complexity : O(1)
Auxiliary Space Complexity: This refers to any extra space used by the algorithm that is independent of the input space and output space. In this case, we only use a constant amount of extra space, specifically for the variables. These variables do not depend on the size of the array and therefore take up constant space. so the auxiliary space complexity is O(1).
Total Space Complexity: This includes the space required for the input, output and extra space used by the algorithm as well. The input array nums[] is of size n, So the space required for input space is O(n). No output space is used. Also, the algorithm takes only constant extra space.
Total Space Complexity = O(n) + O(1) + O(1) = O(n)