Find 2nd Maximum in Array
After identifying the maximum value in an array, the next step in some scenarios is to find the second-highest value. This could represent the runner-up score or the next best option in a dataset. Let’s explore how to determine the second maximum efficiently, ensuring we account for all edge cases.
Given an array of integers, we need to find the 2nd maximum element in the array. The function should print the 2nd maximum value found in the array. If no such value is found print -1.
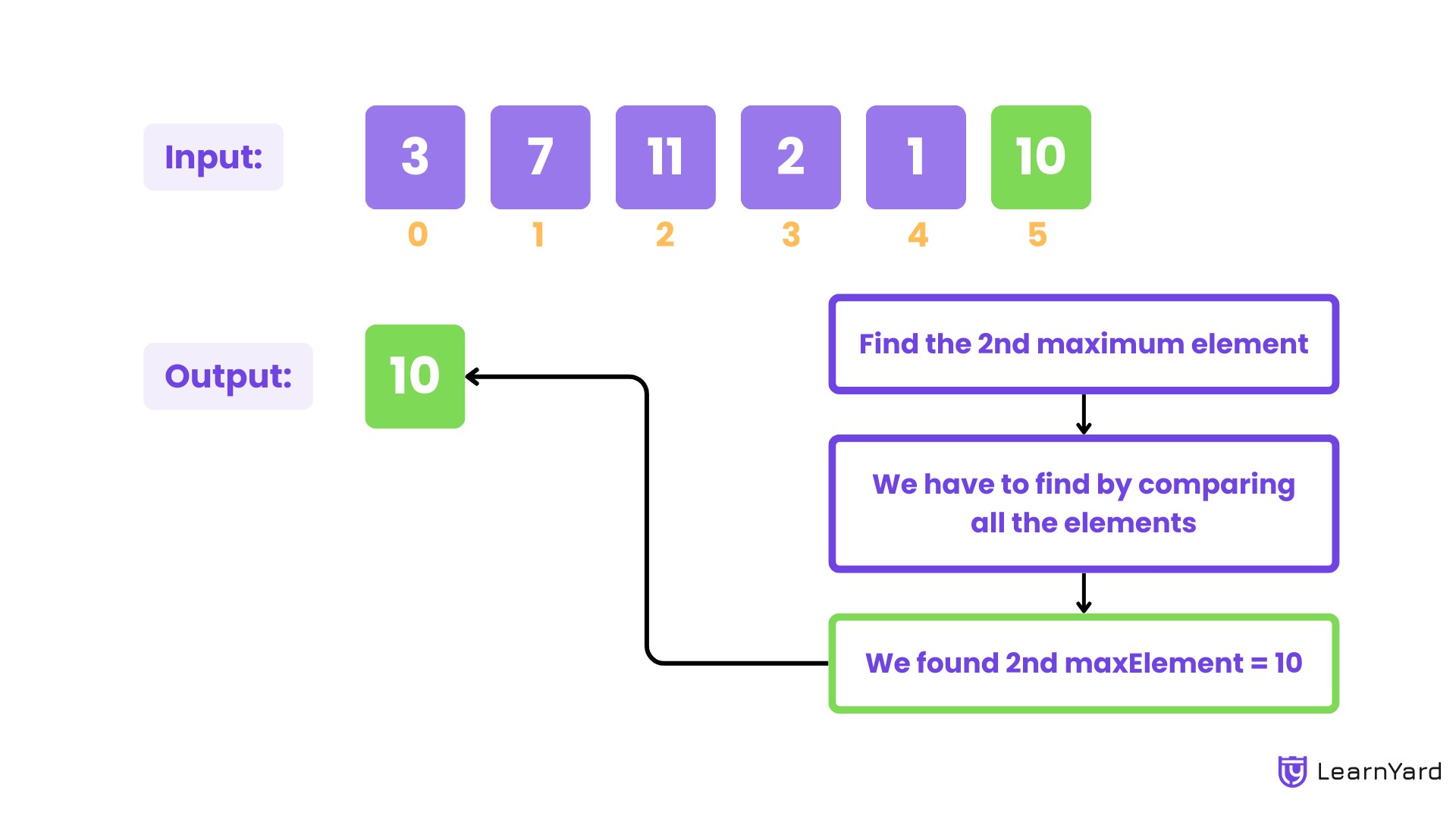
Example
Input: nums = [3, 7, 11, 2, 1, 10]
Output: 10
Explanation: The 2nd maximum element in the array is 10
Input: nums = [3, 4, 1, 5, 2, 5, 1, 10]
Output: 5
Explanation: The 2nd maximum element in the array is 5.
Intuition
Imagine you're back in that queue, but now your goal is to find not just the tallest person but the second tallest.
You start by assuming the first person you see is the tallest. As you move down the line, you keep track of the tallest person you've seen so far. But this time, you also need to keep track of the second tallest person.
How To Think About It
Now, instead of assuming the first person is both the tallest and second tallest, we start with a cleaner and more reliable approach:
Assume both the tallest (maxElement) and the second tallest (secondMaxElement) are initially INT_MIN.
Why?
By initializing both with the smallest possible value, we guarantee that any number in the array will be able to update these placeholders if needed. This approach works even if the array has very small or all negative values, or even duplicate values. It gives us a consistent base to compare every number safely.
However, there's another valid option too:
You can also start maxElement as the first element of the array and secondMaxElement as INT_MIN. This works fine when you’re sure the array has at least one element. In this method, secondMaxElement is still INT_MIN to allow updates from any valid element smaller than maxElement.
Traversal Logic
As you traverse the array:
- If the current number is greater than maxElement, it becomes the new max.
In this case, your previous max becomes your new second max. - If the current number is not equal to maxElement (to handle duplicates) but is greater than secondMaxElement, update only the second max.
Let’s walk through an example:
nums = [3, 7, 11, 2, 1, 10]
maxElement = INT_MIN
secondMaxElement = INT_MIN
Now go through each element and update accordingly. By the end of the loop:
maxElement = 11
secondMaxElement = 10
Done!
What About Duplicates?
Great question! This is something you should clarify with the interviewer right away.
For example, if the input is: [9, 9, 8, 0]
Do we consider the second 9 as the second largest?
Or should we look for the second distinct maximum (which would be 8)?
Always ask: "Should second maximum mean second largest distinct element?"
If Distinct:
Then make sure to skip duplicates of the maximum when determining the second largest.
Why initialize the 2nd Maximum as INT_MIN?
Initializing a secondMaxElement with INT_MIN ensures that any valid array element will be larger, allowing it to be correctly updated during traversal. This approach handles cases where the array may contain very small or uniform values or there is no 2nd larger element. Without this, if no larger value is found, secondMaxElement might remain incorrectly initialized. This guarantees a valid comparison throughout the process.
Approach
The goal of the problem is to find the second maximum element in an array of integers. If there is no valid second maximum (e.g., if the array has fewer than two distinct elements), the function should return -1. Here's a detailed step-by-step approach to solving this problem:
- Initialization:
- Start by initializing two variables maxElement and secondMaxElement to INT_MIN (the smallest possible integer). This ensures that even if all the elements are negative, we have a valid initial comparison comparison point.
- maxElement will keep track of the largest element encountered so far.
- secondMaxElement will store the second largest element.
- Start by initializing two variables maxElement and secondMaxElement to INT_MIN (the smallest possible integer). This ensures that even if all the elements are negative, we have a valid initial comparison comparison point.
- Iterate through the Array:
Loop through each element of the array using a for loop.
- Condition 1 (If element is greater than maxElement):
- If the current element is greater than maxElement, it means we've found a new largest element.
- Update secondMaxElement to the old maxElement (since the previous largest element will now become the second largest).
- Update maxElement to the current element (since it is now the largest).
- Condition 2 (If element is between maxElement and secondMaxElement):
- If the current element is smaller than maxElement but larger than secondMaxElement, update secondMaxElement to the current element.
- This ensures that secondMaxElement always stores the second largest distinct value.
- Edge Case Handling:
- After iterating through the array, if secondMaxElement is still INT_MIN, it means a valid second maximum wasn't found (i.e., the array has fewer than two distinct elements). In this case, print -1.
- Otherwise, print the value of secondMaxElement.
4. Return the Result:
- Print the second maximum element, or -1 if no valid second maximum exists.
Dry Run
- Initialize Variables:
- maxElement = INT_MIN (or -∞ in practical terms)
- secondMaxElement = INT_MIN (or -∞)
- Start Iterating through the Array:First Iteration (i = 0):
- nums[0] = 3
- Check if nums[0] > maxElement → 3 > -∞, which is true.
- So, update secondMaxElement = maxElement = -∞, and then maxElement = nums[0] = 3.
- maxElement = 3, secondMaxElement = -∞
- Second Iteration (i = 1):
- nums[1] = 7
- Check if nums[1] > maxElement → 7 > 3, which is true.
- So, update secondMaxElement = maxElement = 3, and then maxElement = nums[1] = 7.
- maxElement = 7, secondMaxElement = 3
- Third Iteration (i = 2):
- nums[2] = 11
- Check if nums[2] > maxElement → 11 > 7, which is true.
- So, update secondMaxElement = maxElement = 7, and then maxElement = nums[2] = 11.
- maxElement = 11, secondMaxElement = 7
- Fourth Iteration (i = 3):
- nums[3] = 2
- Check if nums[3] > maxElement → 2 > 11, which is false.
- Check if nums[3] > secondMaxElement && nums[3] < maxElement → 2 > 7 && 2 < 11, which is false.
- No changes to maxElement or secondMaxElement.
- maxElement = 11, secondMaxElement = 7
- Fifth Iteration (i = 4):
- nums[4] = 1
- Check if nums[4] > maxElement → 1 > 11, which is false.
- Check if nums[4] > secondMaxElement && nums[4] < maxElement → 1 > 7 && 1 < 11, which is false.
- No changes to maxElement or secondMaxElement.
- maxElement = 11, secondMaxElement = 7
- Sixth Iteration (i = 5):
- nums[5] = 10
- Check if nums[5] > maxElement → 10 > 11, which is false.
- Check if nums[5] > secondMaxElement && nums[5] < maxElement → 10 > 7 && 10 < 11, which is true.
- So, update secondMaxElement = nums[5] = 10.
- maxElement = 11, secondMaxElement = 10
- End of Iteration:
- The loop ends after checking all elements of the array.
- Final Check:
- Since secondMaxElement = 10, which is not equal to INT_MIN, we print the second maximum element: 10.
Final Output:
The second maximum element in the array is 10.
Code for All Languages
C++
// Function to find the 2nd maximum element in the array
void findSecondMaxElement(int nums[], int n) {
// Initialize the maximum and second maximum with the smallest possible value
int maxElement = INT_MIN;
int secondMaxElement = INT_MIN;
// Iterate through the array to find the maximum element
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > maxElement) {
// Update second maximum
secondMaxElement = maxElement;
// Update maximum
maxElement = nums[i];
}
else if (nums[i] > secondMaxElement && nums[i] < maxElement) {
// Update second maximum if it's less than maxElement and
// greater than the current secondMaxElement
secondMaxElement = nums[i];
}
}
// Check if a valid second maximum was found
if (secondMaxElement == INT_MIN) {
// Print -1 if no valid second maximum found
cout << -1 << endl;
}
else {
// Print the 2nd maximum element found in the array
cout << secondMaxElement << endl;
}
}Java
public class LearnYard {
// Function to find the 2nd maximum element in the array
public static void findSecondMaxElement(int[] nums, int n) {
// Initialize the maximum and second maximum with the smallest possible value
int maxElement = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int secondMaxElement = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Iterate through the array to find the maximum element
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > maxElement) {
// Update second maximum
secondMaxElement = maxElement;
// Update maximum
maxElement = nums[i];
}
else if (nums[i] > secondMaxElement && nums[i] < maxElement) {
// Update second maximum if it's less than maxElement and greater than the current secondMaxElement
secondMaxElement = nums[i];
}
}
// Check if a valid second maximum was found
if (secondMaxElement == Integer.MIN_VALUE) {
System.out.println(-1);
}
else {
// Print the 2nd maximum element found in the array
System.out.println(secondMaxElement);
}
}
}
Python
# Function to find the 2nd maximum element in the array
def findSecondMaxElement(nums, n):
# Initialize the maximum and second maximum with the smallest possible value
maxElement = float('-inf')
secondMaxElement = float('-inf')
# Iterate through the array to find the maximum element
for num in nums:
if num > maxElement:
# Update second maximum
secondMaxElement = maxElement
# Update maximum
maxElement = num
elif num > secondMaxElement and num < maxElement:
# Update second maximum if it's less than maxElement and greater than the current secondMaxElement
secondMaxElement = num
# Check if a valid second maximum was found
if secondMaxElement == float('-inf'):
print(-1)
else:
# Print the 2nd maximum element found in the array
print(secondMaxElement)
Javascript
// Function to find the 2nd maximum element in the array
function findSecondMaxElement(nums, n) {
// Initialize the maximum and second maximum with the smallest possible value
let maxElement = -Infinity;
let secondMaxElement = -Infinity;
// Iterate through the array to find the maximum element
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > maxElement) {
// Update second maximum
secondMaxElement = maxElement;
// Update maximum
maxElement = nums[i];
} else if (nums[i] > secondMaxElement && nums[i] < maxElement) {
// Update second maximum if it's less than maxElement and greater than the current secondMaxElement
secondMaxElement = nums[i];
}
}
// Check if a valid second maximum was found
if (secondMaxElement === -Infinity) {
console.log(-1);
} else {
// Print the 2nd maximum element found in the array
console.log(secondMaxElement);
}
}Time Complexity: O(n)
We need to traverse all n elements in the array exactly once. During this single pass through the array, we compare each element to find the maximum and second maximum elements.Each comparison operation (to update maxElement or secondMaxElement) takes constant time, O(1). Since these operations are repeated for every element in the array.The overall time complexity remains O(n).
Space Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space Complexity: This refers to any extra space used by the algorithm that is independent of the input space and output space. In this case, we only use a constant amount of extra space, specifically for the variables maxElement and secondMaxElement. These variables do not depend on the size of the array and therefore take up constant space. so the auxiliary space complexity is O(1).
Total Space Complexity: This includes the space required for the input, output and extra space used by the algorithm as well. The input array nums[] is of size n, So the space required for input space is O(n). No output space is used. Also, the algorithm too takes constant extra space.
Total Space Complexity = O(n) + O(1) + O(1) = O(n)